A family party or a small get together, we all need some stunning music there to lighten up the festive mood. Well, today I’m going to talk about a simple do-it-yourself project that will give you some ‘wire-free’ freedom while you are addressing your invitees. With the following idea you can simply turn your Android phone into a Bluetooth microphone and make yourself heard through a remote loudspeaker. Yes, now you don’t have to shout out just to make yourself audible!
An idea that works with readymade Bluetooth speakers!
Bluetooth microphone presented here is a tricky wireless microphone acceptable to Android mobile devices. This simple wireless audio project design is a poor man’s edition using only inexpensive and easy to grab systems and components.
First of all you’ll have a look at how to get a cheap Bluetooth speaker, and check out for the ones that resemble the mini Bluetooth speaker bought by me from online.
Anyway, never rely on the online seller’s description because the mentioned mini Bluetooth speaker is a cheapo Chinese Bluetooth speaker delivers only a sapless monophonic audio output. This is the link of a detailed breakdown article (prepared by me) included for those interested in knowing more about it – https://www.electroschematics.com/14691/bluetooth-speaker/
Although it’s a bit impaired but still usable for the project covered here (and a real buy at that price)!
Android app(s) & Bluetooth speakers?
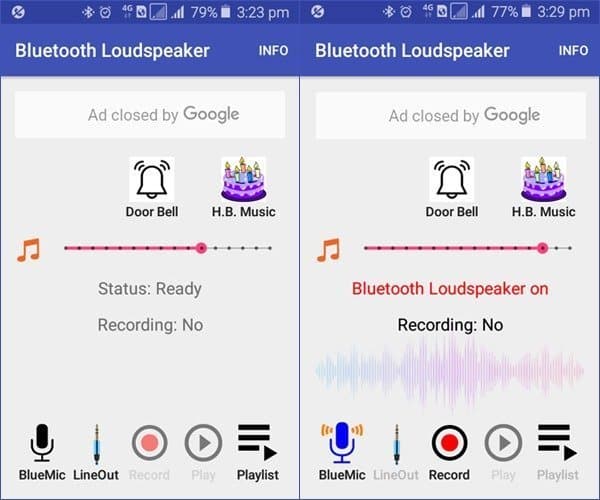
Let me introduce out the latest version of an Android app that works when you have connected the Bluetooth speaker to your Android phone. The “Bluetooth Loudspeaker” (V4.6 by Wimlog) app is a very simple one that does what the name suggests. Once you have connected your phone to the speakers and the app is running, you are good to go. Just tap on the mic and when it turns blue, start talking. The slider is for the master volume control but it also helps you to reduce unwanted noise and echo. The app provides a door chime and happy birthday chime as well. The only thing to remember is that the sound from the speaker will be delayed by a fraction of seconds. The little latency is not a severe problem in most situations. However, if you’re not comfortable, then you can jump freely to other apps as there’re a lot of related apps available on Google Play.
So yes. That’s how you can use your Android phone as a Bluetooth microphone. Well, it might not be good enough for an address aloud for which you’ll have to invest your time (and money) on some technical sweetening. Let me step forward!
Enough room for improvement! Ready for a little complex undertaking?
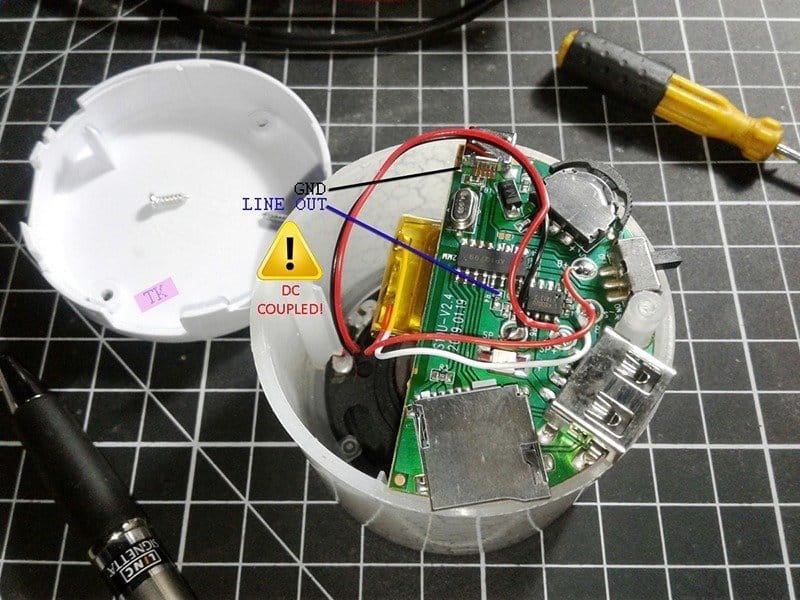
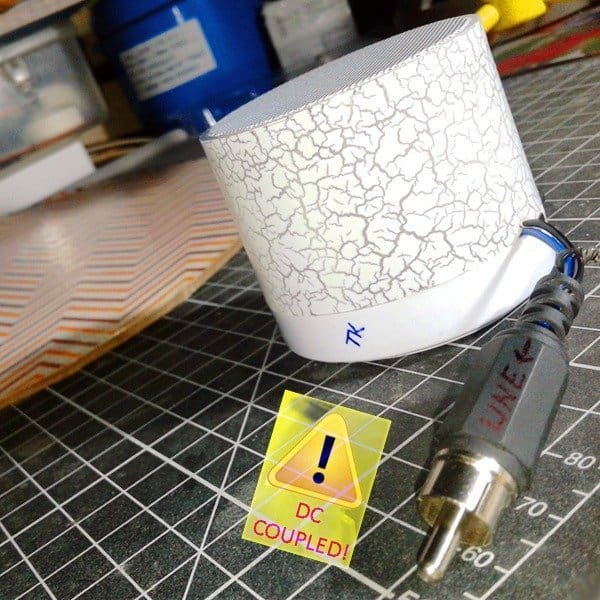
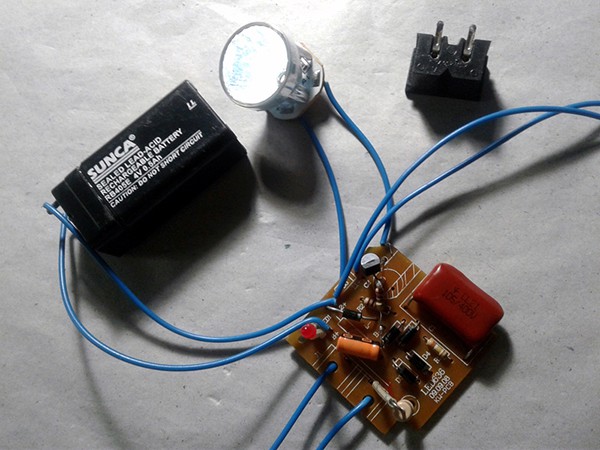
In the mini Bluetooth PCB, you can see a Bluetooth chip and an AF amplifier chip. So, if you’re able to extend the ‘line’ output audio signal path from the Bluetooth chip (that goes to the adjoining amplifier chip), later it’s very easy to boost the audio signal through an external audio power amplifier device. Referring the next photograph will help you to extend that requisite connection if you’re working on the same mini Bluetooth speaker. Else you can use an AF signal tracer to find out the relevant track in other brand bluetooth speakers. Note that here the extension is a dc-coupled audio signal line because of certain technical reasons, and to keep the existing internal loudspeaker’s output intact.
Remember that opening the enclosure of the mini Bluetooth speaker will render the warranty null and void!
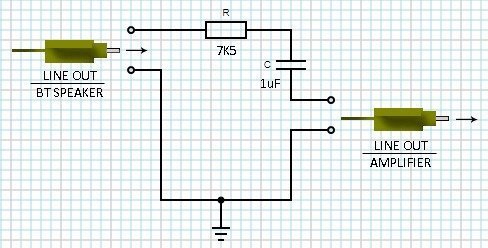
As pointed above, the line-level audio signal output is dc-coupled and hence calls for a suitable adapter circuit for interfacing with input circuitry of most audio power amplifiers. An example circuit of such a simple line out adapter is shown below.
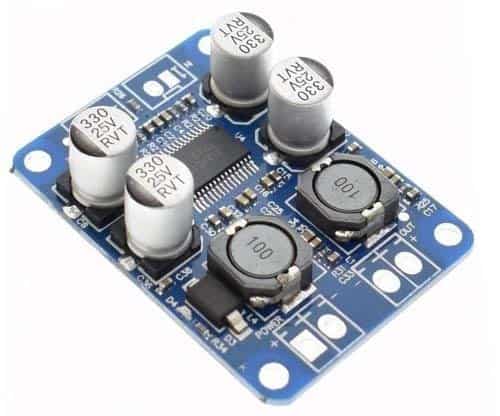
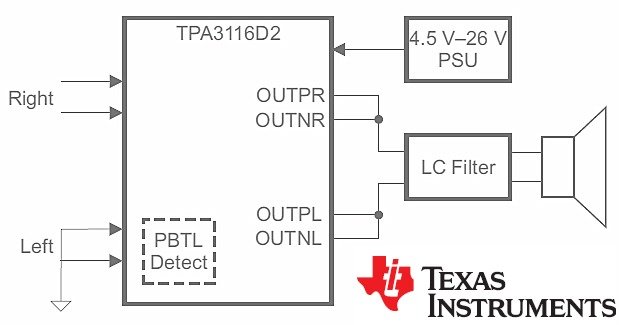
There’re two viable options in front of you to pick the external audio power amplifier – simply buy a commercial one, or build one yourself with easy-to-find components. Considering the latter, it’d be better to choose a good mono power amplifier module to save some time and a few bucks rather than spending an evening with standard discrete parts. Below is an image of a 60W, PBTL mono digital amplifier board based on the TPA3118 IC from Texas Instruments.
The TPA31xxD2 series are stereo efficient, digital amplifier power stage for driving speakers up to 100 W/2 Ω in mono. The TPA3118D2 in particular can deliver 2×30W into a 8Ω BTL Load at 24V. Plainly, BTL (Bridge Tied Load) means no speaker connection to circuit ground, whereas the mono mode here is denoted as PBTL (Parallel Bridge Tied Load). Next figure describes the mono mode of TPA3116D2 in the TPA31xxD2 series!
How to stop hiss/static sound on your Bluetooth audio setup?
If you noticed that your setup makes a very low hiss/static sound, just know that various reasons can cause noise interference to the sound of a Bluetooth speaker. Make an attempt to use the Bluetooth speaker away from other electronics devices like routers, personal computers, etc. in order to avoid radio frequency interference. Since Bluetooth network have limited broadcasting range, the farther you move the paired devices away from each other, the higher the potency for static to occur. Further, if the battery inside your bluetooth speaker or mobile phone is about to empty, this could cause the Bluetooth network connection to weaken to the point that you hear more static than actual audio signal. That’s all for today!
Useful internal & external web links
- https://www.amazon.in/Speakers-Bluetooth-Handsfree-Multicolor-Speaker/dp/B07W7VKC9D
- http://www.wimlog.com/app/bluespk.html
- https://www.codrey.com/electronic-circuits/bluetooth-stereo-audio-adapter-diy-intro-review/
- https://www.amazon.in/Absolute-Native-Electronics-TPA3118-Amplifier/dp/B078W9935Q
- http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tpa3118d2.pdf







I need a interesting project on electronics will you help me to work it out please?
You can find many tried & tested projects here. Anyway, I’d love to hear more about what you’re actually looking for. Feel free to share your thoughts!