What is an Oil Circuit Breaker?
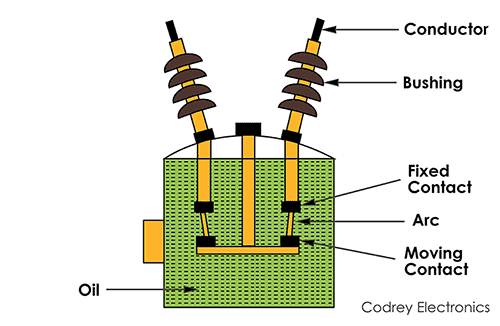
The oil circuit breaker has an insulating oil which is used as an arc quenching medium for arc extinction. Oil has better insulating property than air. It consists of current-carrying contacts enclosed in a metal tank and the tank is filled with the insulating oil. The contacts are made to separate within an oil.
It acts as a good dielectric medium for arc extinction. It is designed for the range of 33kV to 220kV.
Operating Mechanism
The working of the oil circuit breaker is, the contacts are opened when the fault occurs in the system and the arc is developed between the contacts. The heat of the arc evaporates the surrounding oil.
This creates a large bubble of hydrogen that surrounds the arc. The oil surrounding the bubble conducts the heat away from the arc and also contributes to deionization and extinction of the arc.
There are two types of oil circuit breaker:
- Bulk oil Type
- Minimum oil Type (Low oil)
Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker
Bulk oil breakers use a large quantity of oil as an arc quenching medium. The quantity of oil depends on the system voltage. This bulk oil type serves two functions:
- This breaker extinguishes the arc during the opening of the contacts
- It insulates the current-conducting parts from the earthed tank
This has a simple construction and it employs a simple process to separate the contacts under the whole volume of oil in the tank. It is the earliest type of circuit breaker which was developed.
There is no special system for arc control other than the increase in length caused by the separation of contacts. The arc extinction occurs when a certain critical gap between the contacts is reached.
Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker
It is also known as low oil circuit breakers. In bulk oil circuit breakers, only a small quantity of oil is used for the extinction of oil, and the major part of the oil is used for insulation. Also, the quantity of the oil reaches a high value as the voltage increases and it increases the cost, size of the tank, and weight of the circuit breaker.
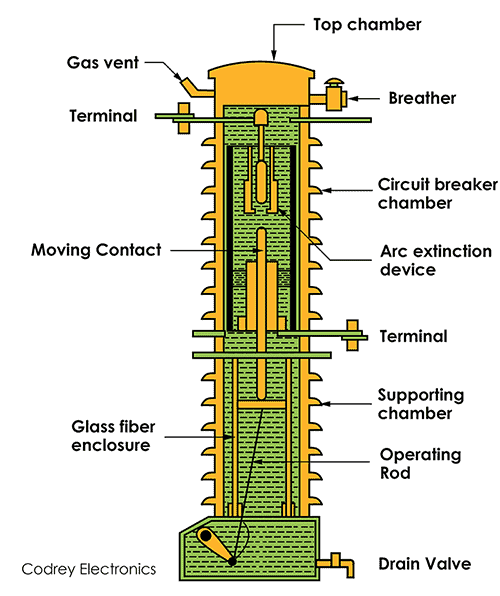
This circuit breaker occupies less space, needs less oil, smaller tank size, and reduces the risk of fire. It consists of two chambers namely circuit breaker chamber (upper) and supporting chamber (lower) which are separated from each other and filled with oil.
The upper chamber is used for arc extinction and the lower is used for insulation purposes.
Both the chambers are surrounded by a porcelain insulator.
When a fault occurs, the moving contact is separated and an arc is formed which causes the high temperature and thus the gas is formed by vaporizing the oil. The gas flowing near the contact causes cooling and splitting of arc and thus the arc is extinguished.
The disadvantage of this type of circuit breaker is the dielectric strength of oil deteriorates rapidly and there is difficulty in removing the gas from contact space.
The applications of Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker makes them suitable for all voltage ranges for the highest breaking capacity.
Maintenance
After the detection of fault current in the circuit breaker, large current flow and burns the contacts due to arcing sequence. Moreover, the carbonization may reduce the dielectric strength of oil and rupture capacity.
Hence proper maintenance of an oil circuit breaker consists of following checkpoints.
- Regularly check the contacts and the dielectric strength of the oil (for every 3 to 6 months).
- Replacement of contact must be done if they are burnt.
- The tripping and the closing circuit should be checked periodically.
- The insulation must be free from carbon particles.
- Verify the volume of oil.
Advantages of using oil as a medium:
- Low cost & easily available
- The oil has good dielectric strength
- Absorption of arc in the oil
- The good cooling properties of gas formed due to decomposing of oil
Disadvantages of using oil as a medium:
- Explosive
- It has a risk of fire
- Requires high maintenance
- Requires periodical replacement
Conclusion
The oil circuit breaker is the oldest type of circuit breaker used. Oil has better insulating property than air. Here, the arc vaporizes the oil into large hydrogen bubbles for the extinction of the arc. The disadvantage of this type is that it requires regular inspection and grounding. It is designed for the range of 33kV to 220kV.
Other than the above types, there are plain break types (single and double), self-blast oil circuit breakers (self-generated pressure oil), and force blast oil circuit breakers.