Most modern electronic circuits and devices consist of different types of capacitors. Electronic newbies, experienced engineers find that these components are quite interesting due to their applications.
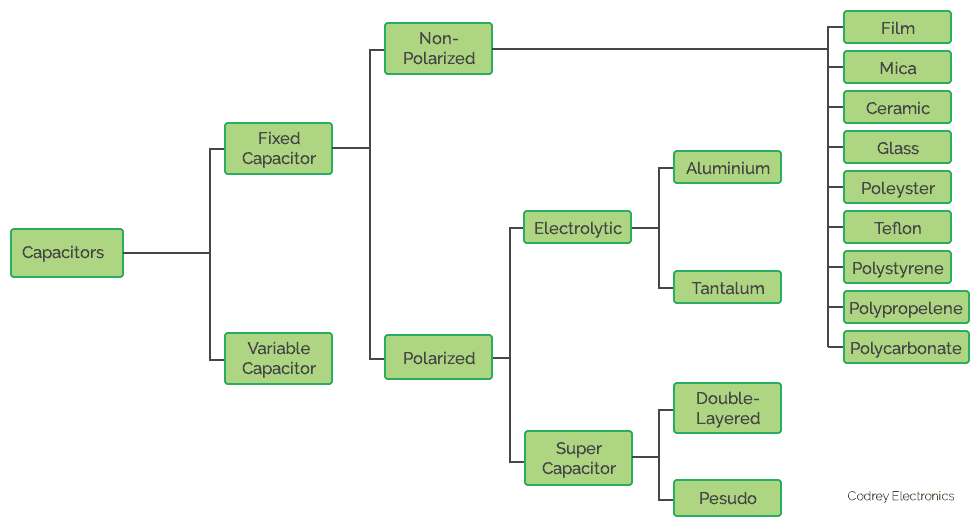
In radio technology, Capacitors can be categorised into fixed capacitor and variable capacitor. Fixed capacitors can be again classified into polarized or electrolytic capacitor and non-polarized capacitors.
Non-polarized capacitors have small capacitance values and have small leakage current. Examples include Ceramic, mica, film capacitors, etc., are some types of non-polarized capacitors. A polarized capacitor has large leakage current. Electrolytic and super capacitors are examples of polarized capacitors.
Capacitor Types
There are different capacitors available depend upon their dielectric material which comes in different shapes and sizes. The most widely used capacitors are ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum and supercapacitors. Let’s look a clear view on categories and types of capacitors.
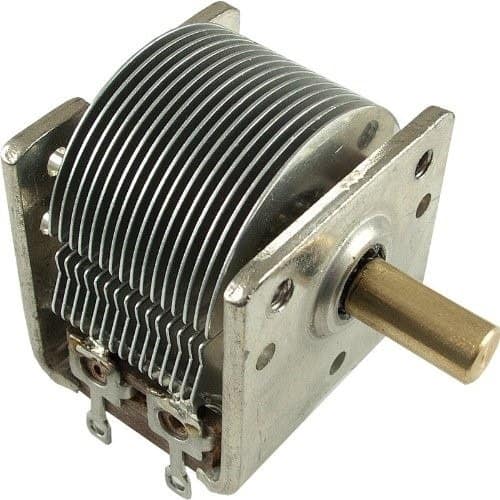
Variable Capacitors
Variable capacitors are nothing but works just like a potentiometer. This is a type of capacitor whose capacitance can be changed mechanically or electronically. It is also called as trimmer capacitor.
The capacitance of a capacitor depends on three factors.
- The area of plates facing each other. By varying the area we have means of varying the capacitance.
- The distance between the plates. By making the distance larger, the capacitance is made smaller and vice versa.
- The kind of dielectric.
In practical, the construction of variable capacitors, use is usually made of the first possibility i.e., a variation of the area of the plates facing each other. Variable capacitors are further subdivided into capacitors for continuous variation (tuning capacitors), and capacitors which only have to be adjusted occasionally (trimmers).
This capacitor gives the value to vary between 10pF to 500pF. The types of variable capacitors are tuning and trimmer capacitors. Used for tuning in radio circuits, transmitters. An important ability of the tuning capacitor to withstand mechanical shocks or vibrations.
The second group of capacitors comprises semi-fixed or trimmers. Here the capacitance is variable but not intended for frequent use. The trimmers are used only to adjust various tuned circuits. Once these capacitors have been adjusted, they are mostly sealed with lacquer so that to all intents and purposes they are fixed capacitors. Trimmers are again divided as Air Trimmer, Ceramic Trimmer, and Wire Trimmer, Mica Trimmer etc.
-
Air Trimmer:
The Air trimmer consists of a cylindrical stator in which a similar cylindrical rotor can be turned on a small screwed rod.
The minimum capacitance is about 3 pF, the maximum capacitance can be 30 or 60 pF. Because air is used as the dielectric, losses in these trimmers are very low. Adjustment is made by means of trimming key made of insulating material (in the form of a box spanner).
-
Ceramic Trimmer :
This trimmer consists of a small ceramic tube which serves as a dielectric. The electrodes (plates) are formed by a tinned copper sleeve and a tinned copper pin which can be screwed into the ceramic sleeve.
Losses in this type of condenser are likewise very low.
-
Wire Trimmer :
The wire trimmer consists of a small ceramic tube, silvered on the inside, and a number of wire turns of wire wound close to each other on the outside.
The layer of silver and the external wire layer form a capacitance which can be reduced by taking turns of wire. The advantage of this type of trimming capacitor is that it is light in weight and small in size, and can be, therefore, mounted directly in the wiring of the set. Moreover, the capacitance is rather large, due to ceramic dielectric, and amounts to a few hundred Pf. The disadvantage is that the capacitance can only be reduced, and not increased so that these are generally used only for few adjusting purposes.
Fixed Capacitors
As can be seen from the name, these capacitors have a fixed capacitance which cannot be changed. The various types of fixed value capacitors are distinguished by their dielectric as described here.
-
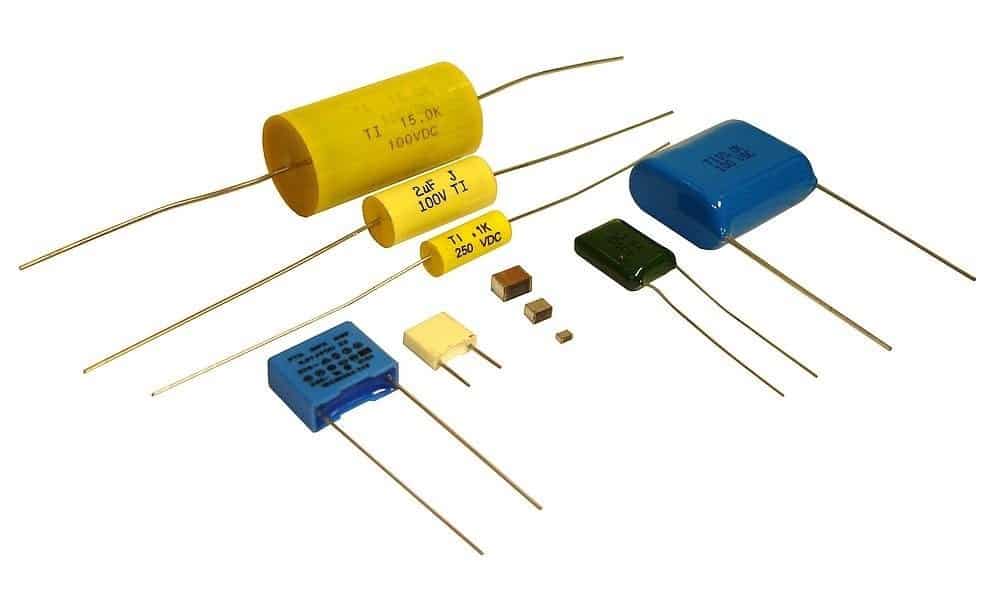
Film Capacitors:
The film capacitors use a plastic film as a dielectric. There is a variety of plastic film which includes polyester, polystyrene, polypropylene, polycarbonate, metallised paper and Teflon are used as a dielectric. Depending upon the type of the film these are classified as paper and metal film capacitors.
These are available in the ranges from 5pF to 100µF. This type of capacitors has smaller tolerances and work under high temperature. They can be used in sample and hold circuits, in snubber circuits used to suppress voltage transients (spikes).
-
Paper capacitors:
Previously these capacitors are used in radio receivers and amplifiers. They are made in two versions, a flat form called block capacitors and a round form called tubular capacitors.
The construction is the same for both. They consist of two aluminum foils (these are very thin layers) between which a few layers of impregnated paper are replaced.
The aluminum foils are the electrodes of the capacitor and the paper is the dielectric. Due to leakage and wide tolerance, these are replaced by polyester capacitors.
-
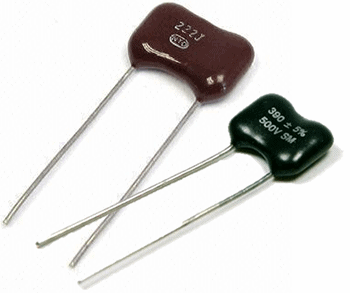
Polyester capacitors:
These capacitors are characterized by their small size, low dielectric loss, and high insulation resistance. They are highly suitable RF based circuits and radio sets.
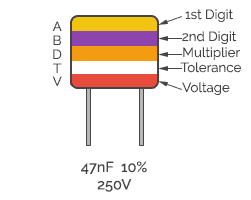
Their construction is similar to paper capacitors but here alternate aluminum and polyester foils are inter-wound in layers. They are available for 160V and 400V ratings with 10% and 20 % tolerances ranging from 1Kpf to 1µF
-
Ceramic Capacitors:
One of the widely used capacitor is ceramic capacitors. This is a non-polarized capacitor. Also called as disc capacitors. In this, the ceramic material is used as a dielectric. This holds a small current and has a small leakage current. They are available from Pico farad to 1 microfarad range. Used for high-frequency applications in audio circuits. These are inexpensive capacitors and have high-frequency performance.
These are classified into class 1, class 2 amplifiers. Applications include filtering, oscillator tuning, EMI suppression, smoothing circuits, and coupling applications.
-
Mica capacitors:
The dielectric of the mica capacitors is made by using thin mica plates of high quality, one side of which is partly covered with a layer of silver.
The value of capacitance is determined by the number of plates, these being joined in parallel. After being assembled, the capacitor is immersed in special wax so that it is protected against the effects of moisture and temperature changes. Because losses in this capacitor are low, they are especially suitable for circuits at high frequencies (oscillator circuits, I.F transformers, etc.) or where low leakage loss is important. These are available in the range of 50pF to 500pF and have working voltage up to 500V. Common applications are used in coupling circuits, ripple filters, resonant circuits. With the recent trend for miniaturization, it is now replaced by ceramic, polystyrene or styroflex capacitors.
-
Air capacitors:
Air is used as a dielectric in air capacitors. The conductive metals are separated by an air gap. There are fixed capacitance air capacitors and variable air capacitors are available. It can be used in tuning radio circuits and can also be used in circuits where low losses are required.
-
Glass capacitors:
Glass is used as the dielectric material in these capacitors and these types of capacitors cost high. Along with glass dielectric, aluminum electrodes are present in these types of capacitors. Plastic encapsulation is done at the end. This type has relatively low capacitance value and can range between a fraction of a Pico farad up to two thousand Pico farads.
It can be used in high power application circuits, where the circuit needs high-temperature zones, circuits that need high tolerances.
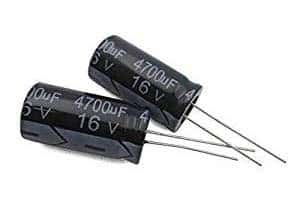
Electrolytic Capacitors:
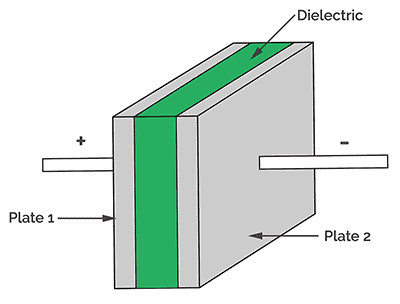
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized. These are also widely used in many applications and have high capacitance values. A metal plate (anode) that forms an insulating oxide layer by anodizing is called dielectric. A solid or semi-solid electrolyte act as a cathode. These have higher capacitance due to their larger anode surface and the thin dielectric oxide layer. These are used when there is a need of high charge storage.
In aluminum electrolytic capacitors, aluminum foil acts as anode insulating an oxide layer which is dielectric and covered by the electrolyte as a cathode. These can be seen in the circuits of power supply for decoupling and switched mode power supply. These are cheaper.
In tantalum type capacitor, tantalum is used as anode and electrolyte as cathode covers an oxide layer. These are a bit high than the aluminum type capacitors.
Super Capacitors:
Conclusion
Well. I hope this tutorial has given a brief overview of different types of capacitor along with their applications. They can be also used in audio circuits for blocking DC current in audio waves. Hence, they are used as smoothening filters to remove unwanted ripples that can damage the electronic circuits.











it is good I like it