I have been using several microwave motion sensor doppler radar modules for years, but in cases where an ultrafine movement detection is demanded, those cheapo modules did not perform well. So I decided to have a look at mmWave radar modules, and got myself a DFRobot SEN0395 mmWave radar sensor for a human presence detection project that may later become part of a home automation system.
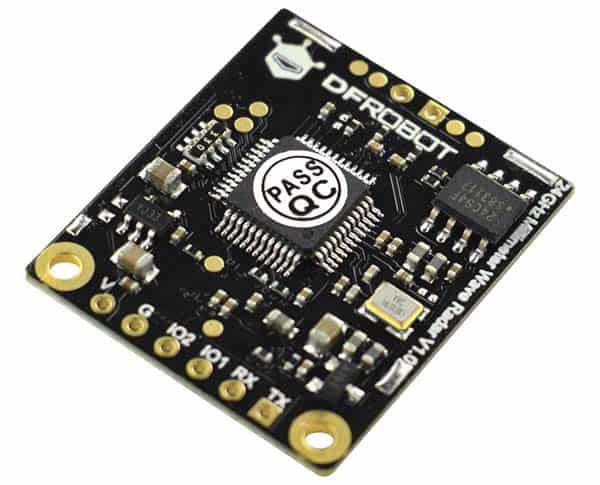

This 24GHz mmWave radar sensor detects the human presence, stationery, and moving people within the detection range of 9m. It employs a separate transmitter and receiver antenna structure, frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW), and continuous wave (CW) multi-mode modulation. This sensor also detects static or stationary human presence such as a sleeping person, and offers serial port and I/O port switch quantity as the two ways provided to the output detection results. Moreover the SEN0395 sensor offers a strong anti-interference ability and is not affected by snow, haze, temperature, humidity, dust, light, and noise.
Well, in this theoretical post, I will share a few points related to mmWave radars, as it is relatively new and not very familiar to many beginners in electronics.
mmWave Radar Sensor
A radar system transmit electromagnetic wave signals that objects in their path then reflect. By capturing the reflected signal, the system can then determine the range, velocity, and angle of the objects. Millimetre wave (mmWave), however, is a special class of radar technology that uses short wavelength electromagnetic waves, i.e. signals with a wavelength that is in the millimetre range. Note that such a sensor system operating at 76–81GHz (with a corresponding wavelength of about 4 mm), will have the ability to detect movements that are as small as a fraction of a millimetre.
On July 13, 2021, the FCC announced a proposal to open up the 60GHz band for commercial mmWave applications. In the FCC proposal, three general applications for mmWave are outlined – indoor communication, outdoor communication, and radar. Interestingly, a single chip can now include the radar, antennas, and computation which allows companies to incorporate mmWave sensors into new products at a much lower cost.
Nowadays, mmWave technology is increasingly used in car radar, cloud radar, radar, and radiometry for concealed weapon detection, high-speed wireless access, ultra-high-speed wireless local area networks and other means of communications, including radar-based communication systems.
The first mainstream mmWave radar project was developed by Google’s ATAP (advanced technology and projects) hardware invention studio. The most recent application is in the second-gen Nest Hub which launched in 2021 with sleep sensing (https://blog.google/products/google-nest/new-nest-hub-soli/).

The big tech goliaths like Google, Amazon, Apple, etc. are not the only ones using mmWave for sleep sensing. Many start-up companies are now focusing on developing sleep sensing products. Another widespread application of mmWave radar sensor is in autonomous mapping and navigation.
Car manufacturers are adding mmWave radar for ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems) as well as occupancy detection. The 4D mmWave radar is very valuable for ADAS as, in addition to sensing in 3D, it can also measure the real-time velocity of each person, car, or other objects it sees.
The mmWave technology applies to a broad range of diverse applications as well. For example, today we can see many mmWave medical devices for monitoring very fine movements (such as breathing and heartbeats) down to 0.1mm or so.
Random Practical Thoughts
In addition to the DFR SEN0395, we can see that nowadays there are many mmWave radar sensors suitable for tasks such as precision presence detection. Let me shed some light on a few.
The DFRobot SEN0395 mmWave is based on LeapMMW HS2xx3A series 24GHz sensor made by the Chinese company Chengdu JiyueShijin Technology Co., Ltd. Another sensor (LeapMMW MR5G21) from this company can be found in Tuya ZigBee Human Presence Sensor ZY-M100 (see below).

Next one is the Aqara Presence Sensor FP1 (see below).

Apart from the commercial products, some other mmWave radar sensors are also in front of the electronics hobbyists and makers. HLK-LD2410 human presence sensing module is a famous part among them.
The LD2410 is a high-sensitivity 24GHz human presence status sensing module developed by Hi-Link Electronics.
This mmWave sensor can be used in indoor scenes to sense whether there is a moving or micro-moving human body in its field of vision. The farthest sensing distance can reach 5metre, and the distance resolution is 0.75m.
The sensor can hand over detection results in real time and it supports both GPIO and UART output ((https://github.com/ESPresense/ESPresense/files/9189632/HLK-LD2410.user.manual.V1.02.pdf).
Going Further
So my next presence detection project starts with a mmWave radar sensor. After getting the DFR mmWave sensor, I did a thorough search and found several mmWave radar modules that fit my plans, although most of them were shockingly overpriced. Anyway, I decided to collect most of them and accordingly placed orders to various online stores.
Sometimes the trick to getting the best was just to wait, and for me waiting is a period of learning!
Credits & References